104 - Cross compiling
To make a program run on the PicoRV32, it has to be written first. The software that is written in this course will be in C. Of course, the processor does not understand C instructions. As you have seen in earlier courses, the C-code is first compiled and then linked to end up with a binary. This binary contains machine code that can be ran on the processor.
If the machine on which the compiler and linker are executed differs from the target machine that is to execute the program, the term cross-compilation is used.
All examples in this course were compiled with the riscv32-unknown-elf-gcc. For more information on installing this toolchain please use Google (e.g. here).
Bare metal
Bare metal programming is writing software that is not running on an Operating System (OS). You probably have done this when (maybe unknowingly) programming an Arduino or another microprocessor.
#include "print.h"
void main(void)
{
print_str("hello world\n");
}The simplest (but still traditional) code that you can imagine is shown here: a simple print of the string hello word. Even with 4 lines of code 2 things should be highlighted.
First of all, no include of stdio.h is done, but “print.h” is included. And secondly, the printing function is print_str() contrary to the traditional printf().
As there is no operating system, we have no access to functions other than to those that we write ourselves. Luckily the repository of the PicoRV32 provides example print functionality. With the include of firmware.h two basic header files are included and 4 forward declarations are done.
// This is free and unencumbered software released into the
// public domain. Anyone is free to copy, modify, publish,
// use, compile, sell, or distribute this software, either
// in source code form or as a compiled binary, for any
// purpose, commercial or non-commercial, and by any means.
#ifndef FIRMWARE_H
#define FIRMWARE_H
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// print.c
void print_chr(char ch);
void print_str(const char *p);
void print_dec(unsigned int val);
void print_hex(unsigned int val, int digits);
#endifWith these four functions, there is an opportunity to print a character, a string (as in a list of characters), a decimal value, or a hexadecimal value. A logical question would be: “Where is my character (or other variable) printed ?”. The answer lies in this line:
*((volatile uint32_t*)OUTPORT) = ch;Let’s break this down for those whose C-skills are a bit rusty. The define OUTPORT makes sure that, everywhere in the code this define is substituted by the 32-bit number 0x10000000. This value is type-cast to an unsigned 32-bit pointer((volatile uint32_t*)). The keyword volatile states that the content of a variable can also be altered from another source. This is important !! Otherwise the optimisation of the C-compiler might optimise-out certain lines of C-code. Finally, that address is dereferenced to target the memory that is located at address 0x10000000.
// This is free and unencumbered software released into the
// public domain. Anyone is free to copy, modify, publish,
// use, compile, sell, or distribute this software, either
// in source code form or as a compiled binary, for any
// purpose, commercial or non-commercial, and by any means.
#include "print.h"
#define OUTPORT 0x10000000
void print_chr(char ch) {
*((volatile uint32_t*)OUTPORT) = ch;
}
void print_str(const char *p) {
while (*p != 0)
*((volatile uint32_t*)OUTPORT) = *(p++);
}
void print_dec(unsigned int val) {
char buffer[10];
char *p = buffer;
while (val || p == buffer) {
*(p++) = val % 10;
val = val / 10;
}
while (p != buffer) {
*((volatile uint32_t*)OUTPORT) = '0' + *(--p);
}
print_chr('\n');
}
void print_hex(unsigned int val, int digits) {
for (int i = (4*digits)-4; i >= 0; i -= 4)
*((volatile uint32_t*)OUTPORT) = \
"0123456789ABCDEF"[(val >> i) % 16];
print_chr('\n');
}Typically, the one function that has to be present in every C-program is the main() function. This function is called by the OS to start of the program. As in bare metal programming there is no OS, some form of booting-process needs to be defined. The PicoRV32 comes with an example assembly file that can be simplified to the script below.
.section .init
.global main
start:
/* zero-initialize all registers */
addi x1, zero, 0
addi x2, zero, 0
addi x3, zero, 0
addi x4, zero, 0
addi x5, zero, 0
addi x6, zero, 0
addi x7, zero, 0
addi x8, zero, 0
addi x9, zero, 0
addi x10, zero, 0
addi x11, zero, 0
addi x12, zero, 0
addi x13, zero, 0
addi x14, zero, 0
addi x15, zero, 0
addi x16, zero, 0
addi x17, zero, 0
addi x18, zero, 0
addi x19, zero, 0
addi x20, zero, 0
addi x21, zero, 0
addi x22, zero, 0
addi x23, zero, 0
addi x24, zero, 0
addi x25, zero, 0
addi x26, zero, 0
addi x27, zero, 0
addi x28, zero, 0
addi x29, zero, 0
addi x30, zero, 0
addi x31, zero, 0
/* set stack pointer */
lui sp, 4
addi sp, sp, 0
/* call main */
jal ra, main
/* break - trap */
ebreakSECTIONS {
.memory : {
. = 0x000000;
*(.init);
*(.text);
*(*);
. = ALIGN(4);
end = .;
}
}This assembly code will be executed first because it is mapped first in the memory space through the linker script (firmware.lds). The assembly file defines there is a label main and then starts of with start label.
This start function sets all the registers of the processor to 0x0. Next it will load the stack pointer register with 0x0000_4000. Then, the main() function is called. After the main function has finished, an ebreak command is execute which will have the PicoRV32 halt and raise the trap signal.
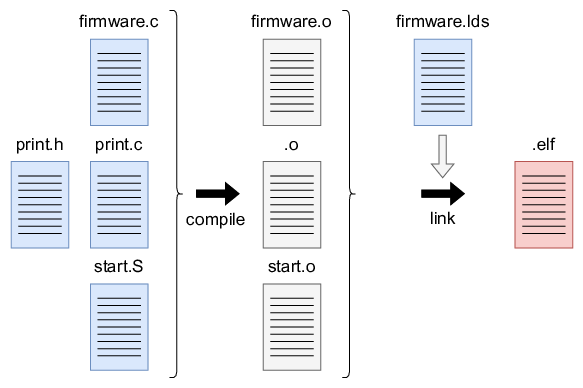
With these 5 files (1 header, 3 C files and a linker script) the final binary file can be generated. This binary is in the Executable and Linkable Format (.elf)
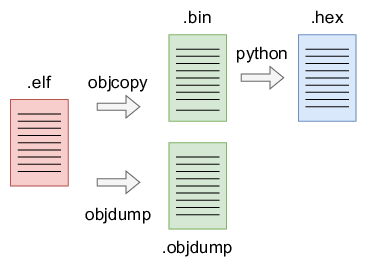
Conversion to human-readable and to FPGA-compatible
After running the tool chain, an .elf file is generated. It might become useful to understand what is going on in this file (as humans). Secondly, this file needs to be loaded to the FPGA implementation of the RISC-V.
… to human-readable
The generated binary file can be disassembled again. Doing this allows us to read what was eventually generated by the compiler. The riscv32-toolbox comes with a program riscv32-unknown-elf-objdump. This can be used to achieve a disassembly by using the -D option.
An option to generate this file is present in the Makefile and the result should look something like this.
firmware.elf: file format elf32-littleriscv
Disassembly of section .memory:
00000000 <start>:
0: 00000093 li ra,0
4: 00000113 li sp,0
8: 00000193 li gp,0
c: 00000213 li tp,0
10: 00000293 li t0,0
14: 00000313 li t1,0
18: 00000393 li t2,0
1c: 00000413 li s0,0
20: 00000493 li s1,0
24: 00000513 li a0,0
28: 00000593 li a1,0
2c: 00000613 li a2,0
30: 00000693 li a3,0
34: 00000713 li a4,0
38: 00000793 li a5,0
3c: 00000813 li a6,0
40: 00000893 li a7,0
44: 00000913 li s2,0
48: 00000993 li s3,0
4c: 00000a13 li s4,0
50: 00000a93 li s5,0
54: 00000b13 li s6,0
58: 00000b93 li s7,0
5c: 00000c13 li s8,0
60: 00000c93 li s9,0
64: 00000d13 li s10,0
68: 00000d93 li s11,0
6c: 00000e13 li t3,0
70: 00000e93 li t4,0
74: 00000f13 li t5,0
78: 00000f93 li t6,0
7c: 00004137 lui sp,0x4
80: 00010113 mv sp,sp
84: 1c8000ef jal ra,24c <main>
88: 00100073 ebreak
0000008c <esns_nop>:
8c: 00000013 nop
90: 00008067 ret
00000094 <print_chr>:
94: 100007b7 lui a5,0x10000
98: 00a7a023 sw a0,0(a5) # 10000000 <end+0xffffd98>
9c: 00008067 ret
000000a0 <print_str>:
a0: 10000737 lui a4,0x10000
a4: 00054783 lbu a5,0(a0)
a8: 00079463 bnez a5,b0 <print_str+0x10>
ac: 00008067 ret
b0: 00150513 addi a0,a0,1
b4: 00f72023 sw a5,0(a4) # 10000000 <end+0xffffd98>
b8: fedff06f j a4 <print_str+0x4>
000000bc <print_dec>:
bc: fe010113 addi sp,sp,-32 # 3fe0 <end+0x3d78>
c0: 00812c23 sw s0,24(sp)
c4: 00410413 addi s0,sp,4
c8: 00912a23 sw s1,20(sp)
cc: 01212823 sw s2,16(sp)
d0: 00112e23 sw ra,28(sp)
d4: 00050493 mv s1,a0
d8: 00040913 mv s2,s0
dc: 02049c63 bnez s1,114 <print_dec+0x58>
e0: 03240a63 beq s0,s2,114 <print_dec+0x58>
e4: 10000737 lui a4,0x10000
e8: fff40413 addi s0,s0,-1
ec: 00044783 lbu a5,0(s0)
f0: 03078793 addi a5,a5,48
f4: 00f72023 sw a5,0(a4) # 10000000 <end+0xffffd98>
f8: ff2418e3 bne s0,s2,e8 <print_dec+0x2c>
fc: 01c12083 lw ra,28(sp)
100: 01812403 lw s0,24(sp)
104: 01412483 lw s1,20(sp)
108: 01012903 lw s2,16(sp)
10c: 02010113 addi sp,sp,32
110: 00008067 ret
114: 00a00593 li a1,10
118: 00048513 mv a0,s1
11c: 0a8000ef jal ra,1c4 <__umodsi3>
120: 00140413 addi s0,s0,1
124: fea40fa3 sb a0,-1(s0)
128: 00a00593 li a1,10
12c: 00048513 mv a0,s1
130: 04c000ef jal ra,17c <__udivsi3>
134: 00050493 mv s1,a0
138: fa5ff06f j dc <print_dec+0x20>
0000013c <print_hex>:
13c: fff58593 addi a1,a1,-1
140: 00000737 lui a4,0x0
144: 00259593 slli a1,a1,0x2
148: 22870713 addi a4,a4,552 # 228 <__modsi3+0x30>
14c: 100006b7 lui a3,0x10000
150: 0005d463 bgez a1,158 <print_hex+0x1c>
154: 00008067 ret
158: 00b557b3 srl a5,a0,a1
15c: 00f7f793 andi a5,a5,15
160: 00e787b3 add a5,a5,a4
164: 0007c783 lbu a5,0(a5)
168: ffc58593 addi a1,a1,-4
16c: 00f6a023 sw a5,0(a3) # 10000000 <end+0xffffd98>
170: fe1ff06f j 150 <print_hex+0x14>
00000174 <__divsi3>:
174: 06054063 bltz a0,1d4 <__umodsi3+0x10>
178: 0605c663 bltz a1,1e4 <__umodsi3+0x20>
0000017c <__udivsi3>:
17c: 00058613 mv a2,a1
180: 00050593 mv a1,a0
184: fff00513 li a0,-1
188: 02060c63 beqz a2,1c0 <__udivsi3+0x44>
18c: 00100693 li a3,1
190: 00b67a63 bgeu a2,a1,1a4 <__udivsi3+0x28>
194: 00c05863 blez a2,1a4 <__udivsi3+0x28>
198: 00161613 slli a2,a2,0x1
19c: 00169693 slli a3,a3,0x1
1a0: feb66ae3 bltu a2,a1,194 <__udivsi3+0x18>
1a4: 00000513 li a0,0
1a8: 00c5e663 bltu a1,a2,1b4 <__udivsi3+0x38>
1ac: 40c585b3 sub a1,a1,a2
1b0: 00d56533 or a0,a0,a3
1b4: 0016d693 srli a3,a3,0x1
1b8: 00165613 srli a2,a2,0x1
1bc: fe0696e3 bnez a3,1a8 <__udivsi3+0x2c>
1c0: 00008067 ret
000001c4 <__umodsi3>:
1c4: 00008293 mv t0,ra
1c8: fb5ff0ef jal ra,17c <__udivsi3>
1cc: 00058513 mv a0,a1
1d0: 00028067 jr t0
1d4: 40a00533 neg a0,a0
1d8: 0005d863 bgez a1,1e8 <__umodsi3+0x24>
1dc: 40b005b3 neg a1,a1
1e0: f9dff06f j 17c <__udivsi3>
1e4: 40b005b3 neg a1,a1
1e8: 00008293 mv t0,ra
1ec: f91ff0ef jal ra,17c <__udivsi3>
1f0: 40a00533 neg a0,a0
1f4: 00028067 jr t0
000001f8 <__modsi3>:
1f8: 00008293 mv t0,ra
1fc: 0005ca63 bltz a1,210 <__modsi3+0x18>
200: 00054c63 bltz a0,218 <__modsi3+0x20>
204: f79ff0ef jal ra,17c <__udivsi3>
208: 00058513 mv a0,a1
20c: 00028067 jr t0
210: 40b005b3 neg a1,a1
214: fe0558e3 bgez a0,204 <__modsi3+0xc>
218: 40a00533 neg a0,a0
21c: f61ff0ef jal ra,17c <__udivsi3>
220: 40b00533 neg a0,a1
224: 00028067 jr t0
228: 3130 fld fa2,96(a0)
22a: 3332 fld ft6,296(sp)
22c: 3534 fld fa3,104(a0)
22e: 3736 fld fa4,360(sp)
230: 3938 fld fa4,112(a0)
232: 4241 li tp,16
234: 46454443 fmadd.q fs0,fa0,ft4,fs0,rmm
238: 4700 lw s0,8(a4)
23a: 203a4343 fmadd.s ft6,fs4,ft3,ft4,rmm
23e: 4728 lw a0,72(a4)
240: 554e lw a0,240(sp)
242: 2029 jal 24c <main>
244: 2e38 fld fa4,88(a2)
246: 2e32 fld ft8,264(sp)
248: 0030 addi a2,sp,8
...
0000024c <main>:
24c: 00000537 lui a0,0x0
250: 25850513 addi a0,a0,600 # 258 <main+0xc>
254: e4dff06f j a0 <print_str>
258: 6568 flw fa0,76(a0)
25a: 6c6c flw fa1,92(s0)
25c: 6f77206f j 73152 <end+0x72eea>
260: 6c72 flw fs8,28(sp)
262: 0a64 addi s1,sp,284
264: 0000 unimp
...… to FPGA-compatible
Next to ‘decompiling’ the binary .elf file to a human-readable representation, it can also be translated to a flat text format. This can be achieved with a Python script makehex.py.
An option to generate this hex dump is present in the Makefile and the result should look something like this.
00000093
00000113
00000193
00000213
00000293
00000313
00000393
00000413
00000493
00000513
00000593
00000613
00000693
00000713
00000793
00000813
00000893
00000913
00000993
00000a13
00000a93
00000b13
00000b93
00000c13
00000c93
00000d13
00000d93
00000e13
00000e93
00000f13
00000f93
00004137
00010113
1c8000ef
00100073
00000013
00008067
100007b7
00a7a023
00008067
10000737
00054783
00079463
00008067
00150513
00f72023
fedff06f
fe010113
00812c23
00410413
00912a23
01212823
00112e23
00050493
00040913
02049c63
03240a63
10000737
fff40413
00044783
03078793
00f72023
ff2418e3
01c12083
01812403
01412483
01012903
02010113
00008067
00a00593
00048513
0a8000ef
00140413
fea40fa3
00a00593
00048513
04c000ef
00050493
fa5ff06f
fff58593
00000737
00259593
22870713
100006b7
0005d463
00008067
00b557b3
00f7f793
00e787b3
0007c783
ffc58593
00f6a023
fe1ff06f
06054063
0605c663
00058613
00050593
fff00513
02060c63
00100693
00b67a63
00c05863
00161613
00169693
feb66ae3
00000513
00c5e663
40c585b3
00d56533
0016d693
00165613
fe0696e3
00008067
00008293
fb5ff0ef
00058513
00028067
40a00533
0005d863
40b005b3
f9dff06f
40b005b3
00008293
f91ff0ef
40a00533
00028067
00008293
0005ca63
00054c63
f79ff0ef
00058513
00028067
40b005b3
fe0558e3
40a00533
f61ff0ef
40b00533
00028067
33323130
37363534
42413938
46454443
43434700
4728203a
2029554e
2e322e38
00000030
00000537
25850513
e4dff06f
6c6c6568
6f77206f
0a646c72
00000000Overall toolflow